A septic system diagram visualizes the main components of your home’s wastewater system—including house plumbing, septic tank, distribution box, and drain field—and shows how they connect. Understanding this diagram is vital for effective maintenance, troubleshooting, and communication with septic professionals.
- A septic system diagram shows how plumbing, tank, and field connect and function together.
- Using the diagram helps homeowners detect issues, plan upgrades, and communicate with service pros.
- Component knowledge is recommended by the EPA and critical for system care.
- Regular review of your diagram supports successful maintenance and safe home wastewater management.
Table of Contents
Introduction: The Critical Role of Septic System Diagram
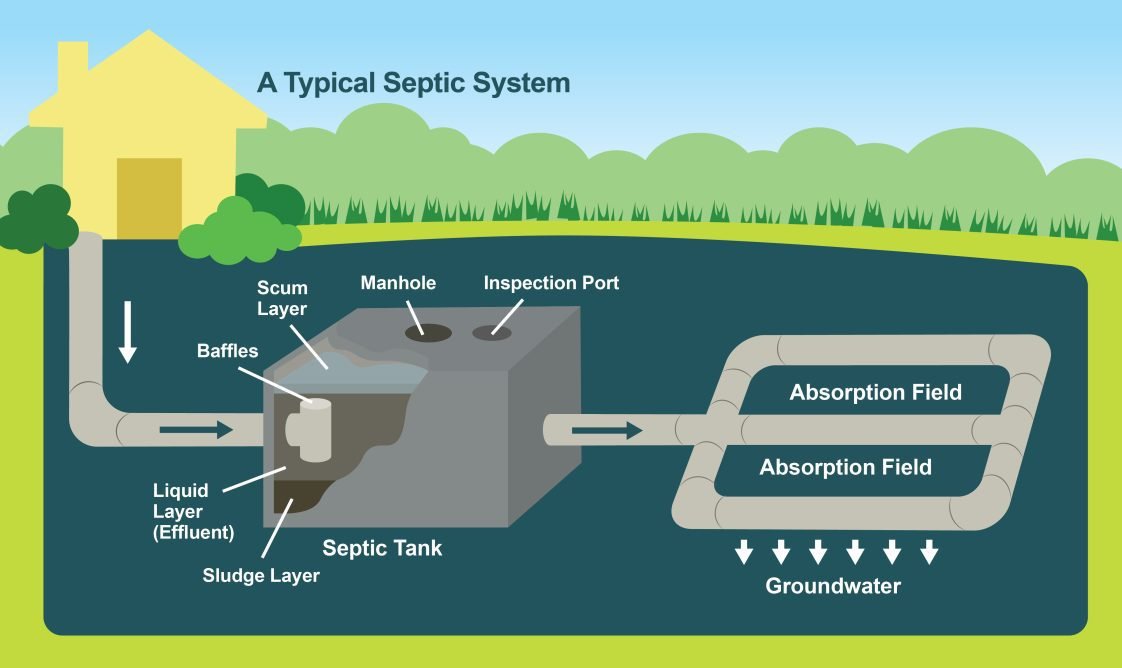
Understanding how a septic system works begins with a clear septic system diagram. This visual guide connects directly to the main pillar of home wastewater management by illustrating all septic system components and their functions. A septic system diagram helps homeowners visualize the flow of wastewater from the house, through the septic tank, and into the drain field. Without clear knowledge of this layout, diagnosing problems, performing maintenance, or communicating with service providers becomes challenging.
Deep Dive: Understanding Septic System Diagram
Detailed Definition and Components
A septic system diagram displays the arrangement and interconnection of key components. Understanding these helps keep your system running efficiently and in accordance with EPA guidelines.
| Component | Purpose |
|---|---|
| House Plumbing Pipes | Transport wastewater from sinks, toilets, and showers to the septic tank |
| Septic Tank | Buried, watertight tank where solids settle and effluent is partially treated |
| Distribution Box | Distributes effluent evenly to the drain field lines |
| Drain Field (Leach Field) | Soil-based area where effluent is further filtered and absorbed |
| Vent Pipe | Allows safe release of gases |
| Access Risers & Clean-Out Ports | Provide maintenance and inspection entry points to the tank and pipework |
How It Functions Within the Larger System
The diagram tracks the path of household wastewater from indoor plumbing through the septic tank. Solids settle at the bottom, a scum layer floats to the top, and the partially treated effluent exits in the middle. This effluent flows via the distribution box into the drain field, where soil naturally filters and treats it before it returns to the groundwater.
Visual Breakdown
[Visual schematic: house drain → septic tank → distribution box → drain field with labeled parts]
Practical Applications and Real-World Scenarios
Use Case 1: Diagnosing a Septic Tank Backup
When experiencing backups, homeowners can use the septic system diagram to track flow, identify access points, and efficiently isolate whether the cause is a blockage or full tank.
Use Case 2: Planning a Septic System with Drain Field Replacement
Upgrading or replacing your septic system? Contractors and homeowners alike use the diagram to map out excavation, component positions, and compliance with local regulations—streamlining both design and permitting.
Industry-Specific Applications
Environmental engineers, plumbers, and home inspectors rely on detailed septic diagrams to design custom systems for unique soils, communicate system function to clients, and predict possible points of failure.
Implementation Guide
Step-by-Step Process
- Assess property layout and soil suitability. Evaluate lot size, setbacks, and soil percolation rates.
- Design the system layout. Specify tank size, distribution box location, and drain field dimensions based on home size and soil data.
- Dig and install the septic tank and piping.
- Install distribution box and drain field trenches or chambers.
- Connect house plumbing to septic tank inlet.
- Backfill carefully. Avoid damaging pipes and tank using correct materials and compaction.
- Test for flow and filter operation. Ensure there are no leaks or blockages—professional inspection is advised.
Required Tools and Resources
- Excavation equipment
- Pipe cutting, joining, and fitting tools
- Septic tank, distribution box, piping
- Soil percolation and inspection kits
- Permits and local health department guidance
Typical Timeline and Milestones
| Stage | Typical Time |
|---|---|
| Design & Permitting | 1–3 weeks |
| Excavation & Installation | 3–5 days |
| Inspection & Startup | 1–2 days |
Integration and Optimization
How This Connects to Septic System Maintenance Best Practices
Understanding your system’s layout supports critical maintenance tasks. For best results, follow our detailed septic system maintenance guide : regular pumping, baffle inspection, and drain field care all rely on clear diagrams.
How This Connects to Troubleshooting Septic System Problems
A diagram makes troubleshooting efficient—helping you or your septic technician pinpoint the location of issues like clogs, leaks, or failing field lines. Explore targeted troubleshooting at Septic System Troubleshooting .
Optimization Tips for Maximum Efficiency
- Maintain the proper slope in drainage pipes to prevent solids buildup.
- Limit water use to reduce hydraulic load on your system.
- Routinely inspect risers and clean-outs as shown in your diagram.
- Install effluent filters if compatible—these help prevent solids from reaching the drain field, extending system longevity.
Troubleshooting This Specific Aspect
Common Problems and Symptoms
- Slow drains or backups inside the house
- Odors near the septic tank or drain field
- Soggy, saturated soil over the drain field
- Unusual plant/algae growth in nearby water bodies
Diagnostic Flowchart
[Visual diagnostic flowchart: symptom → likely issue → key checks → recommended action]
Solutions for Each Issue
- Slow drains: Check for clogged pipes or have the septic tank pumped.
- Odors: Inspect tank seals and check vent pipes for blockages.
- Wet drain field: Limit water usage and consult a professional for possible restoration or replacement.
- Nearby water pollution: Have the system inspected and repaired immediately to avoid contamination of wells and waterways.
When to Call a Professional
If problems persist after basic steps, or if you notice sewage on the ground surface, contact a licensed septic contractor via Local Septic Service Providers to prevent health hazards and costly repairs.
Maintenance Schedule and Best Practices
Daily/Weekly Tasks
- Conserve water to reduce pressure on your system.
- Never flush grease, chemicals, or hazardous waste.
Monthly/Quarterly Checks
- Monitor for slow drains or odd smells—early signs of problems.
- Inspect easily accessible risers and clean-outs for buildup or leaks.
Annual Review and Updates
- Schedule professional septic tank pumping every 3–5 years, depending on household size and usage.
- Have a certified professional inspect tank baffles and the drain field.
- Review your system layout diagram to ensure accuracy, especially before and after system repairs or major changes.
Conclusion and Pathways Forward
A septic system diagram is a vital reference for any homeowner. It clarifies how all components function and connect, ensuring successful maintenance, efficient troubleshooting, and effective communication with professionals. For complete home wastewater care, revisit our main septic system guide and explore detailed troubleshooting at the links above.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does a septic system diagram typically include?
A standard septic system diagram includes house plumbing pipes, septic tank, distribution box, drain field, vent pipes, and all maintenance access points—showing the flow path of wastewater through each stage.
How can I use a septic system diagram for troubleshooting?
By referencing the diagram, you can pinpoint component locations, isolate blockages, locate access and clean-out points, and communicate effectively with septic service professionals.
What is the difference between a conventional and an aerobic septic system diagram?
| System Type | Main Features Shown in Diagram |
|---|---|
| Conventional | Tank, distribution box, and drain field. Waste breakdown mainly by anaerobic bacteria. |
| Aerobic | Tank, aeration chamber for oxygen treatment, advanced effluent treatment stage, possibly a different drain field structure. |
How often should I update or review my septic system diagram?
Review your septic diagram annually and update it after any major repairs, additions, or system upgrades to maintain an accurate record for maintenance and regulatory compliance.
Can I install a septic system using only a diagram?
While a diagram is essential for understanding layout and planning, professional system design, permitting, and installation are required for compliance with local health and environmental codes (see CDC recommendations).
What are the key signs that my drain field is failing?
Soggy surface soil, persistent odors, and pooling wastewater above the drain field indicate possible failure and should prompt immediate inspection and remediation.

Leave a Reply